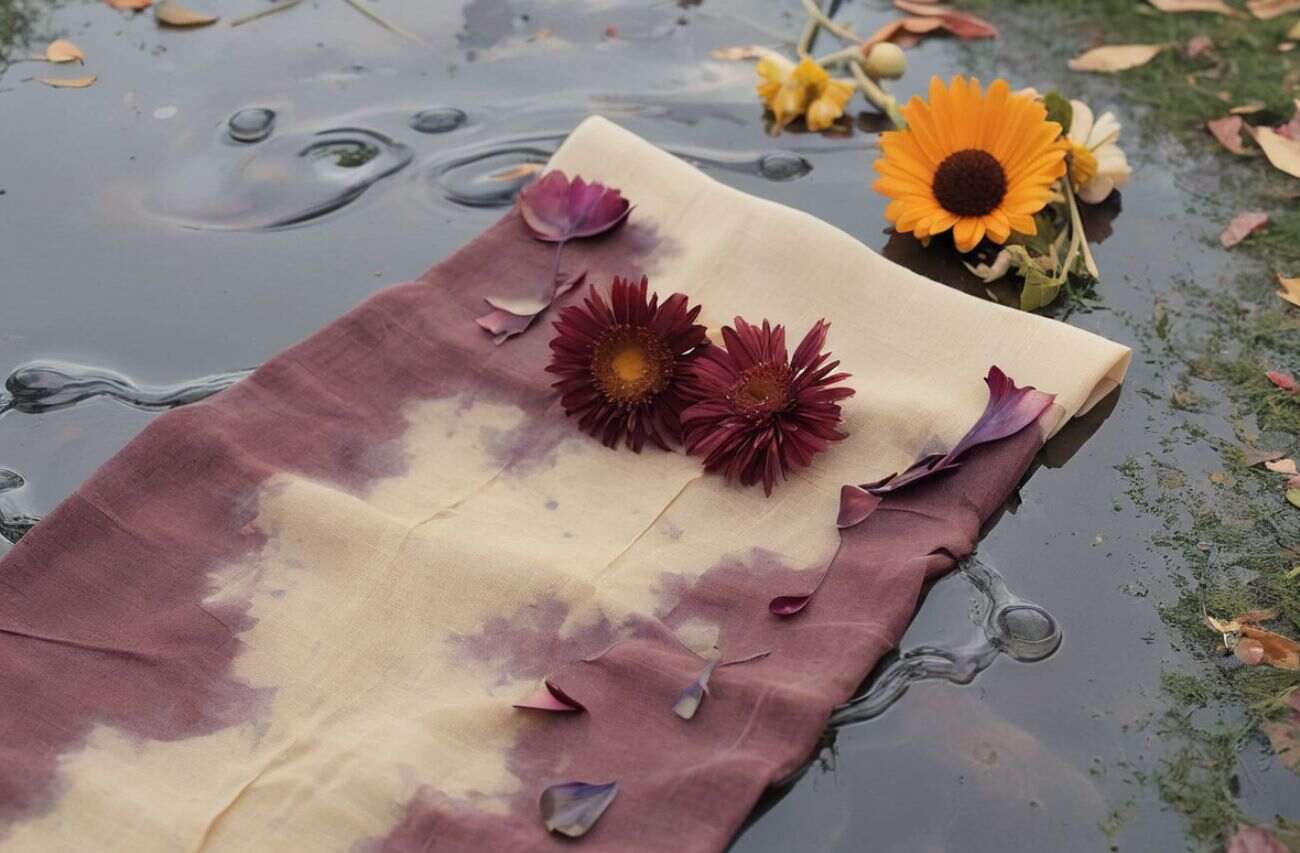

Dye safe, live bright: Say no to synthetic dyes
very time we wear a vibrant shirt or sip from a colorful mug, we might be unknowingly contributing to a hidden environmental crisis. Synthetic dyes, ubiquitous in our daily lives, might make our world brighter, but they are dimming the future of our planet by posing severe threats.
These dyes contain harmful components like heavy metals and formaldehyde, which can contaminate water sources, harm aquatic life, and pose health risks to humans, including allergies, respiratory issues, and even cancer.
Addressing the issues associated with synthetic dyes is crucial for the health of our environment and ourselves. With the textile industry at the top, the food, and pharmaceutical industries are among the largest consumers of synthetic dyes, and the wastewater produced during dyeing processes often contains billions of tons of these harmful chemicals. This untreated wastewater pollutes rivers and oceans, leading to a cascade of ecological damage that affects the entire food chain, from microorganisms to humans.
Legislation and sustainable technologies are essential to combat this issue, but individual choices also play a significant role. By opting for sustainable dyes, we can reduce our environmental footprint and protect our health.
With this blog, we, at Qalara, aim to educate readers on the dangers of synthetic dyes and present safer, eco-friendly alternatives that allow us to enjoy vibrant colors without compromising our planet’s future.
Join us as we explore how to dye safe and live bright!
The threat of synthetic dyes
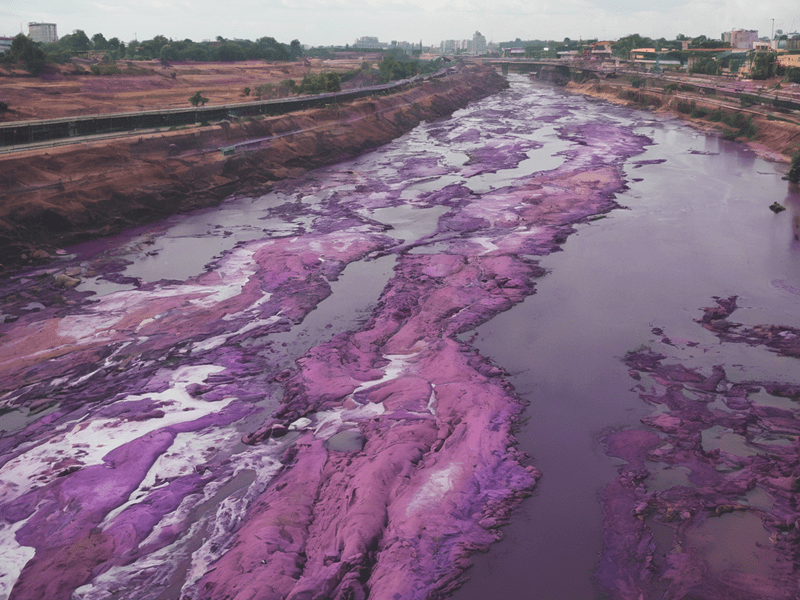

Synthetic dyes are a vibrant, universal feature of modern life, coloring everything from textiles and foods to pharmaceuticals. Yet, their widespread use masks significant environmental and health concerns.
1. Water contamination: As per a study, each year, the textile industry alone generates about 70 billion tons of dye-laden wastewater. Another research highlights that currently, up to 80% of dye-containing industrial wastewater created in low and middle-income countries are released untreated into waterways, causing severe environmental damage. These dyes block sunlight, disrupting photosynthesis in aquatic plants and altering entire ecosystems. To tackle this problem, innovative solutions like membrane-based nano-scale filtration are gaining attention, offering a promising method to effectively filter out these pollutants. However, there is also a crucial need for stricter legislation to ensure that colorants are removed before reaching public sewage systems or natural waterways.
2. Impact on plant and animal health: Synthetic dyes don’t just affect water; they also harm plant and animal health. In aquatic environments, dyes can inhibit photosynthesis, which affects the food chain from microalgae to fish. Algae, the foundation of aquatic ecosystems, struggle to grow and thrive, leading to broader ecological imbalances. Fish exposed to these dyes may experience respiratory issues, liver damage, and reduced reproductive health. As dyes can bioaccumulate in fish tissue, they pose a health risk to both wildlife and humans who consume contaminated fish.
3. Human health risks: Synthetic dyes, commonly used in textiles and cosmetics, pose significant risks to human health. These dyes often contain harmful chemicals such as azo compounds, which can release carcinogenic amines when metabolized in the body. Prolonged exposure to synthetic dyes has been linked to various health issues, including skin irritation, respiratory problems, and even cancer. Additionally, some synthetic dyes can disrupt endocrine function, potentially affecting hormone levels and reproductive health. As awareness of these risks grows, there is a stronger push towards safer, natural alternatives in consumer products.
4. Negative impact on soil microbial communities: In soil, synthetic dyes disrupt essential microbial communities that support plant growth and nutrient cycling. Pollutants from dye-containing wastewater can alter soil chemistry, hinder microbial activity, and negatively affect plant development. This disruption can lead to stunted plant growth, reduced seed germination, and diminished crop yields.
In summary, while synthetic dyes offer aesthetic benefits, their environmental and health impacts highlight the urgent need for more sustainable practices and better waste management. Shifting towards eco-friendly alternatives could significantly reduce these adverse effects and protect both our planet and our well-being.
The textile industry's role
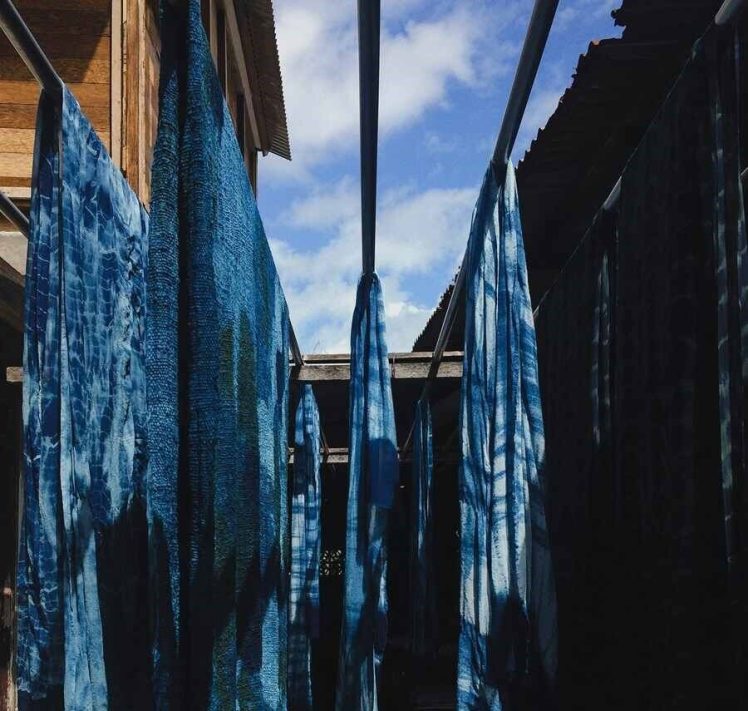

Humans have been dyeing fabric for millennia, with the earliest record dating back to 3500 BC. Until 1856, when the chemist William Henry Perkins accidentally discovered synthetic dyes, all dyes were made from natural pigments and oils. Today, a whopping 90% of our clothes are dyed synthetically, a practice that poses significant environmental risks.

One major issue with textile dyeing is the excessive water consumption and pollution involved. Dyeing cotton, for example, uses approximately 125 liters of water per kilogram of cotton fibers. Beyond the water itself, dyeing requires substantial energy to heat water and steam for the desired finish.
A lack of transparency in chemical use in synthetic dyes compounds these problems. A 2016 report by KEMI revealed that nearly 30% of chemicals used in textile manufacturing and dyeing were confidential, meaning potentially toxic substances could be used without disclosure. This not only pollutes water sources but also poses health risks to those wearing the garments.
As per a market survey, the global textile industry is a major consumer of synthetic dyes, using around 70% of the worldwide dyestuff market. With over 10,000 types of dyes synthesized annually, the industry produces about one million tons of synthetic dyes each year. A significant portion, 60 to 80%, are AZO dyes, many of which are carcinogenic.
What drives this massive consumption of synthetic dyes? The industry’s insatiable demand for vibrant and long-lasting colors, the endless variety of hues, and the constant push for new seasonal shades. Synthetic dyes meet these needs efficiently, offering consistency, durability, and cost-effectiveness, making them indispensable to modern textile production.
However, the environmental cost is staggering. The textile industry generates about 70 billion tons of dye-containing wastewater annually, making it one of the most polluting industries. Major textile hubs like China, India, and Bangladesh face severe water pollution issues due to inadequate wastewater treatment regulation and facilities, posing health risks to local communities. The industry’s heavy reliance on synthetic dyes and insufficient regulation underscores the urgent need for more sustainable dyeing practices.
Also read: The causes & dangers of over-production
Now, let us explore the current processes used to decontaminate dye wastewater and evaluate their effectiveness.
Current remediation technologies
The textile industry employs a variety of methods to treat dye wastewater, including physical, chemical, and biological processes. Despite these efforts, the sector remains largely unorganized, exacerbated by the lack of stringent global regulations. This results in inconsistent application and effectiveness of wastewater treatment methods, contributing to ongoing environmental challenges. Here’s an overview of the existing technologies:
1. Physical treatment: This method physically separates contaminants from water, often using materials like activated carbon or nanoparticles.
● Adsorption: Uses materials like activated carbon to attract and hold dye molecules. While effective, this method is often costly.
● Filtration: Membrane-based processes like reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration separate dyes and other pollutants from water, producing reusable water but sometimes generating foul odors and insoluble waste.
● Ion-exchange: Involves swapping harmful ions in the wastewater with harmless ones using ion-exchange resins, which can be expensive.
● Oxidation: Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) use strong oxidizers to break down dyes, although they can produce hazardous by-products.
2. Chemical treatment:
● Coagulation/Flocculation: Adds chemicals to wastewater to form clumps of contaminants that can be easily removed. This is effective for removing suspended solids but often requires further treatment.
● Ozonation: Uses ozone gas to oxidize and break down dye molecules, with the advantage of no sludge generation but high costs and sensitivity to environmental conditions.
3. Biological treatments: Utilize microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi to degrade dye pollutants. This method is environmentally friendly and cost-effective but can be slow and affected by high concentrations of toxic substances.
● Biodegradation/Bioremediation: Microorganisms naturally break down harmful compounds, converting them into less harmful or even beneficial products.
4. Combinatorial treatment: This is a multi-step approach that combines various methods to achieve thorough decontamination. Typically, chemical treatments are followed by biological processes and finalized with physical methods to ensure complete purification.
5. Moving towards sustainable solutions:
To address the limitations of current methods, the industry needs to advance toward more sustainable and site-specific solutions. Decentralized treatment systems, tailored to local needs, will enhance efficiency and reduce costs. A multi-pronged approach, combining various technologies, is going to be essential for effective results.
Global regulatory efforts are crucial in setting standards and driving innovation in wastewater treatment. Effective regulations are necessary for positive change. Given the vast amounts of synthetic dyes used by the textile industry, we must ask: Can we realistically achieve sustainable development goals and net-zero targets without implementing stringent rules and regulations?
Moreover, significant potential exists for creating new revenue streams through wastewater processing and recycling. By recovering materials and reusing treated water, industries can reduce their environmental impact while enhancing economic viability.
Also read: How are big brands pledging to reduce waste
Alternatives to synthetic dyes
While these remediation methods focus on recycling water and can save tons of it, we must consider whether recycling is truly the best approach. The five principles of waste management emphasize refusing, reducing, reusing, and repurposing before resorting to recycling, which should ideally be the last option. Refusing and reducing are undoubtedly the best strategies.
So, how can we apply these principles to synthetic dyes? By utilizing alternative dyes and methods! Let’s explore some sustainable alternatives to synthetic dyes.
Natural dyes
When talking about alternatives to dyes, natural dyes top the list, and for all the right reasons! Natural dyes are derived from plant-based ingredients making them both biodegradable and environmentally friendly. Since they are extracted from natural sources, the resulting wastewater is non-toxic, posing no threat to water bodies or aquatic life. Since the beginning of time, natural dyes have been the only option for coloring fabrics and yarns, showcasing their long-standing use and effectiveness in textile dyeing.
Some of the ingredients used to make natural dyes are:
– Madder root: Known for its rich red and pink hues
– Indigo: A plant-based dye that produces a deep blue color
– Turmeric: Provides a vibrant yellow shade
– Onion skins: Yields colors ranging from yellow to orange
– Walnut hulls: Used for brown and black tones
– Beetroot: Creates various shades of pink and purple
– Cochineal: An insect-based dye that produces a bright red color
– Hibiscus flowers: Offers a range of pink to purple shades
– Avocado pits and skins: Produce soft pinks and peachy hues
– Pomegranate rinds: Yield yellow to greenish colors
– Chamomile: Known for its light yellow shades
– Eucalyptus leaves: Can produce colors from yellow to green
Historically, the age-old Indian crafts, such as Ajrakh block printing, Ikat, Dabu printing, lacquer-coated Channapatna toys, and even Pattachitra paintings, relied exclusively on natural dyes. These dyes, derived from plant-based ingredients, were integral to the traditional methods and aesthetics of these crafts. However, over time, artisans began adopting synthetic dyes to remain competitive in a market increasingly driven by mass production. The demand for vibrant, cost-effective options led to the widespread use of synthetic dyes, which could achieve brighter colors and were more economical than their natural counterparts. As a result, the use of humble natural dyes declined, unable to compete with the intense hues and lower costs of synthetic alternatives.
As more customers become aware of the negative impacts of current dyeing techniques, a gradual shift is taking place. Increasingly, innovators, companies, and organizations are experimenting with natural dyes to revive their relevance in response to modern demands and needs. This resurgence is driven by a collective effort to develop sustainable and eco-friendly dyeing solutions, ensuring that natural dyes can compete with synthetic options while meeting contemporary standards for vibrancy and cost-effectiveness.
Returning to these age-old practices and methods seems like the best option. However, natural dyes offer limited color options, and achieving vibrant hues like hot pink is nearly impossible. Additionally, color fastness is a concern with plant-based dyes. Despite these challenges, eco-conscious brands are embracing natural dyes for their sustainable collections. Nevertheless, a more permanent solution is needed if we aim to completely eliminate harmful, toxic synthetic dyes.
One notable name in the field of 100% natural, eco-friendly, and biodegradable dye innovation is Truetone Ink from India. Truetone Ink proudly positions itself as the industrial expert on herbal dyes, a technology they have revived from ancient history and the roots of our soil. Their dyes are not only beautiful and natural but also provide a sustainable alternative to the harmful petroleum-based dyes that have damaged our planet and our health. By embracing Truetone Ink’s herbal dyes, we can take a significant step towards healing our environment and promoting well-being.
Qalara offers a diverse selection of eco-friendly products dyed with natural ingredients. Explore the range now!
Also read: What makes Qalara a planet-friendly choice
Azo-free dyes
Azo-free dyes are a category of colorants that do not contain azo compounds, which are synthetic chemicals characterized by their nitrogen-nitrogen double bond (N=N). Azo dyes are commonly used in the textile industry due to their vibrant colors and cost-effectiveness. However, many azo dyes release aromatic amines when they break down, which are known to be carcinogenic and harmful to the environment. Let us understand what makes azo-free dyes a better choice.
1. Environmental and health benefits: This method physically separates contaminants from water, often using materials like activated carbon or nanoparticles.
● Non-toxic nature: Azo-free dyes do not release harmful aromatic amines, making them a safer alternative for both the environment and human health. They reduce the risk of exposure to toxic and carcinogenic substances.
● Biodegradability: These dyes are often more biodegradable compared to conventional azo dyes, leading to less environmental pollution and a reduced ecological footprint.
● Reduced water pollution: Azo-free dyes minimize the contamination of water bodies. Since they break down more easily and are less toxic, they contribute less to the water pollution typically caused by the textile dyeing process.
● Sustainable production: Many azo-free dyes are derived from natural sources or are produced using more sustainable methods, further contributing to their eco-friendly profile.
2. Industry adoption and innovation:
● Increased use: As awareness of the environmental impact of synthetic dyes grows, more brands and manufacturers are adopting azo-free dyes. This shift is driven by consumer demand for safer, more sustainable products.
● Regulatory support: Regulations in many countries are becoming stricter regarding the use of harmful chemicals in dyes. Azo-free dyes help companies comply with these regulations, ensuring safer products for consumers.
In summary, azo-free dyes present a compelling alternative to traditional synthetic dyes, offering significant health and environmental benefits. As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, the use of azo-free dyes is a positive step forward in reducing the harmful impact of textile production on our planet.
Innovative dyeing practices across the globe
While it is true that innovations like plastic and synthetic dyes have caused significant harm, the human brain has always been a source of remarkable innovation, and these advancements aren’t always the doom and gloom that some might believe. Fortunately, as we continue to research ways to make natural dyes as effective as synthetic ones, matching their color variety and fastness, many other innovations hold promise for our quest to eliminate toxic synthetic dyes.
1. ColorZen: ColorZen revolutionizes cotton dyeing with its patented pre-treatment technology, drastically reducing water usage by 90%, energy consumption by 75%, and chemical usage by 90%. This innovative approach not only enhances production efficiency but also offers a sustainable and eco-friendly solution for the textile industry.
2. AirDye: AirDye is a groundbreaking technology that enables water-free textile printing and dyeing, drastically reducing water usage by up to 95% and energy consumption by 86%. By using a high-heat process to transfer dyes from recycled paper to fabric, AirDye offers a sustainable, efficient, and environmentally friendly solution for the textile industry.
3. DyeCoo: DyeCoo’s revolutionary CO₂ technology offers the world’s first 100% water-free and chemical-free textile dyeing process, utilizing supercritical CO₂ to achieve vibrant colors with 98% dye uptake. This sustainable solution reduces environmental impact while providing textile manufacturers with geographical freedom from water sources and compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
4. Faber Futures: Faber Futures leverages synthetic biology to program bacteria to produce a wide range of colors for both synthetic and natural fibers, promoting sustainable and regenerative textile practices. By integrating technical, societal, and ecological realms, Faber Futures pioneers resilient systems for a biotech-led bio-economy.
5. Werewool: Werewool creates regenerative fibers using engineered microbes that produce proteins, offering performance without plastics and color without water pollution. Inspired by nature, such as the bright pink protein from Discosoma Coral, Werewool’s innovative approach integrates these proteins into bacteria, which are then woven into vibrant, sustainable textiles.
6. We aRe SpinDye: We aRe SpinDye revolutionizes textile dyeing by melting color pigments with recycled polyester before spinning it into yarn, eliminating the need for water and reducing overall water usage by 75%. This innovative method, used by H&M in their Conscious Exclusive collection, offers a sustainable solution for coloring textiles.
7. Huue.: Huue. produces sustainable, biosynthetic indigo dye for the denim industry using sugar instead of toxic chemicals, eliminating significant water pollution. Their bioengineering technology creates eco-friendly dyes, offering a greener solution with five times less toxicity than conventional indigo.
8. Living Color X PUMA: Living Colour is a pioneering biodesign project in the Netherlands that uses pigment-producing bacteria to dye textiles, offering a sustainable alternative to artificial dyes. Collaborating with PUMA in 2020, they created the first-ever bacterial-dyed sports collection, showcasing the potential for eco-friendly textile coloration.
9. Woolmark-certified Tintoria di Quaregna X Victoria Beckham: Tintoria di Quaregna’s NATURALE process uses over 200 natural ingredients to dye wool and other natural fibers, creating a wide range of colors without chemicals, additives, or dye powders. As the first natural dyer to gain Woolmark certification, this Italian dyehouse leads in sustainable textile dyeing, sourcing materials globally and primarily from Italy. Victoria Beckham used Woolmark licensee Tintoria di Quaregna’s natural dyeing process for the luxury label’s latest knitwear collection.
10. Marimekko X Natural Indigo: Marimekko, the Finnish textile company, has launched a new collection of garments, bags, and home items, showcasing prints dyed with natural colors provided by Natural Indigo, a startup based in Finland.
11. Ralph Lauren X Dow: Ralph Lauren is partnering with Dow to enhance the sustainability of dyed cotton through the “Ecofast Pure” treatment. This collaboration introduces a manual to open-source an advanced dyeing process that significantly reduces water, chemical, and energy usage in cotton dyeing.
12. SU.RE. Project by the Indian government: In 2020, the Indian government launched Project SU.RE. (Sustainable Resolution) to drive long-term sustainability in the textile industry. This initiative is the Indian apparel industry’s largest commitment to move towards sustainable fashion and it aims to align with Sustainable Development Goals by enhancing water and energy access, fostering resilient infrastructure, and promoting responsible consumption and production.
Future challenges & conclusion
Despite promising advancements, the textile industry faces challenges in adopting sustainable dyeing technologies. High competition and rising raw material costs pressure manufacturers to keep prices low, complicating efforts to optimize eco-friendly solutions and maintain affordability for consumers. For these innovations to effectively replace the deeply entrenched synthetic dyes, they must become cost-effective and scalable.
As synthetic dyes continue to wreak havoc on our planet, the urgency to transition to sustainable alternatives has never been clearer. By supporting and adopting eco-friendly dyeing practices, you play a pivotal role in reshaping the future of textiles. Explore and invest in innovative, sustainable dye products on Qalara today.
Remember, our choices today are not just about the clothes we wear but the world we leave behind. What impact will our decisions make on the future of our planet? The power to transform the industry, and the planet, rests in our hands!
It is time we dye safe and live bright!
~ Written by Utkarsha Rai








Surbhi
Amazing read!
You don’t usually get all the information including sustainable dye initiatives all in one article.